
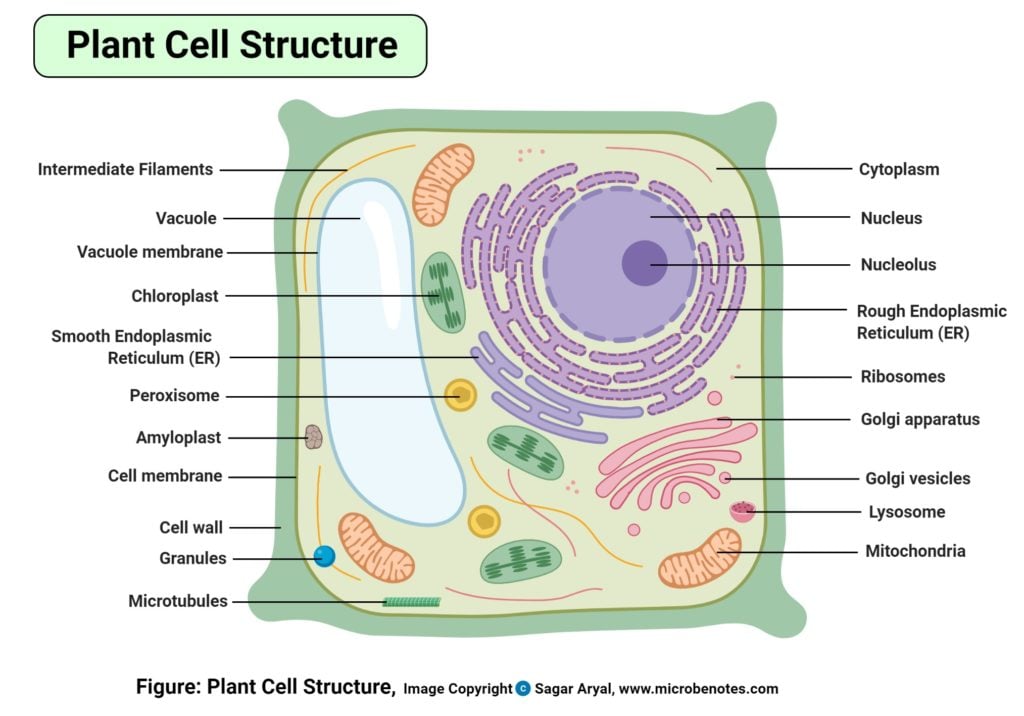
Eukaryotic cells, in particular, form the foundation for many organisms, including humans, plants, and animals. Ques.Enter the Microscopic World with Interactive Cell Diagram LabellingĮvery living organism is made up of cells, and understanding these tiny building blocks can offer a deeper insight into the complex world of biology. However, there are several exceptions to this for example, the absence of mitochondria and a nucleus in red blood cells and the lack of mitochondria in the oxymonad Monocercomonoides species. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria, a Golgi apparatus, an endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes are located. Eukaryotic: Eukaryotes are a cell or organisms that have a clearly defined nucleus.Prokaryote life started over 4 billion years ago, feeding off the early carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, steam, nitrogen, hydrogen, and ammonia atmosphere. Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotic: Prokaryotes are microscopic single-celled organism that doesn’t have a separate nucleus with a membrane or specialized organelles.Organisms having single cells are called unicellular organisms Peroxisomes are round spherical organelles with a single membrane that carry the oxidation process of the cell.Īns. Microfilaments are the rounded structures on the cell that forms a part of the cytoskeleton.Cilia and Flagella are the hair-like structures on the cell membrane of the animal cell diagram. It supports the membrane to carry out the entry and exit process of nutrients.Micro Tubules are responsible for supporting, storing and transporting procedures of cell.Intermediate Filaments are the fibrous materials of the cell responsible for maintaining the rigidity of cell.

It consists of 9 bundles of microtubules found in animal cells. The centrosome is an organelle with a thick bundle of cells.As seen in the diagram of animal cell, it mainly separates chromosomes from the rest of the cell and is also known as a nuclear envelope. Nuclear Membraneis the membrane that encloses the cell nucleus.The nucleus coordinates with different cell activities such as growth and reproduction. It is responsible for storing hereditary material – DNA and other genetic materials in the cell. The nucleus, enclosed by different membranes, is the brain of the cell.It is a medium in which chemical reactions take place in the animal cell. It is responsible for the expansion, growth, and replication of the cell. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like structure spread all over the cell containing all the cell organelles in it.With hair-like structures – cilia and flagella, the cell membrane controls the entry and exit of nutrients into the animal cell. The Cell Membrane is the thin semi-permeable layer of phospholipids surrounding the cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
